-
Bacterial Infection
ACNE VULGARIS
Hormone imbalance in the body at puberty influences the activity of the sebaceous gland, causing an increased production of sebum. The sebum may be retained within the sebaceous ducts, causing congestion and bacterial infection of the surrounding tissues.
Appearance: Inflammation of the skin, accompanied by comedones, pustules and papules.
Site: Commonly on the face, the nose, the chin and the forehead. Acne may also occur on the chest and back.
TREATMENT: Medical – oral antibiotics may be prescribed, as well as medicated creams. With medical approval, regular salon services may be given to cleanse the skin deeply and also to stimulate the blood circulation.
TINEA CORPORIS OR BODY RINGWORM
A fungal infection of the skin.
Appearance: Small scaly red patches, which spread outwards and then heal from the centre, leaving a ring.
Site: The trunk of the body, the limbs and the face.
Treatment: Medical – using a fungicidal cream. Oral anti-fungal medication is necessary if there are several infection sites.
Future prospects
If the infection is treated it will usually disappear relatively quickly, but the treatment should normally be continued for a while after the rash improves to eradicate the fungus.
What can be done to prevent an infection?
Fungi that can cause a skin infection are present everywhere and are difficult to avoid. However, if possible, refrain from direct skin-to-skin contact with people or animals suspected of having a fungal infection.
…
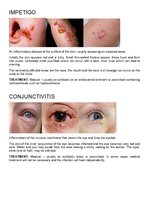
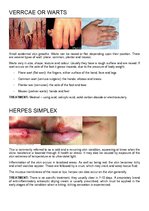
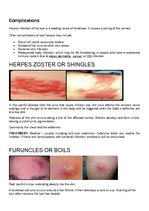
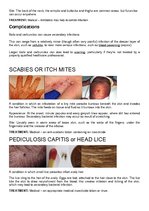
IMPETIGO, CONJUNCTIVITIS, VERRCAE OR WARTS, HERPES SIMPLEX, HERPES ZOSTER OR SHINGLES, FURUNCLES OR BOILS, SCABIES OR ITCH MITES, PEDICULOSIS CAPITIS or HEAD LICE, PEDICULOSIS PUBIS or PUBIC LICE, PEDICULOSIS CORPORIS or BODY LICE, ACNE VULGARIS, TINEA CORPORIS OR BODY RINGWORM