-
Indonesia
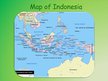
Indonesia is an archipelagic country extending 5,120 kilometers from east to west and 1,760 kilometers from north to south. It encompasses an estimated 17,508 islands, only 6,000 of which are inhabited. It comprises five main islands : Sumatra, Java, Borneo (known as “Kalimantan” in Indonesia), Sulawesi and New Guinea.
Mountains ranging between 3,000 and 3,800 meters above sea level can be found on the islands of Sumatra, Java, Bali, Lombok, Sulawesi, and Seram. The country's largest mountains are located in the Jayawijaya Mountains and the Sudirman Mountains in Papua. The highest peak ,Puncak Jaya, also known as Mount Carstenz, which reaches 4,884 meters, is located in the Sudirman Mountains.
The country has numerous mountains and about 400 volcanoes, from which approximately 150 are active.
Climate
The climate of Indonesia is almost entirely tropical. The uniformly warm waters that make up 81 % of Indonesia's area ensure that temperatures on land remain fairly constant, with the coastal plains averaging 28°C, the inland and mountain areas averaging 26 °C, and the higher mountain regions, 23 °C. Temperature varies little from season to season, and Indonesia experiences relatively little change in the length of daylight hours from one season to the next; the difference between the longest day and the shortest day of the year is only forty-eight minutes. This allows crops to be grown all year round.
The extreme variations in rainfall are linked with the monsoons. Generally speaking, there is a dry season (June to September), influenced by the Australian continental air masses, and a rainy season (December to March) that is the result of mainland Asia and Pacific Ocean air masses. …
Interenstākie fakti par Indonēziju. Ģeogrāfija, klimats, daba, vēsture, sabiedrība pilitika, izglītība.